Introduction & OS Structure
Chapter 1: Introduction
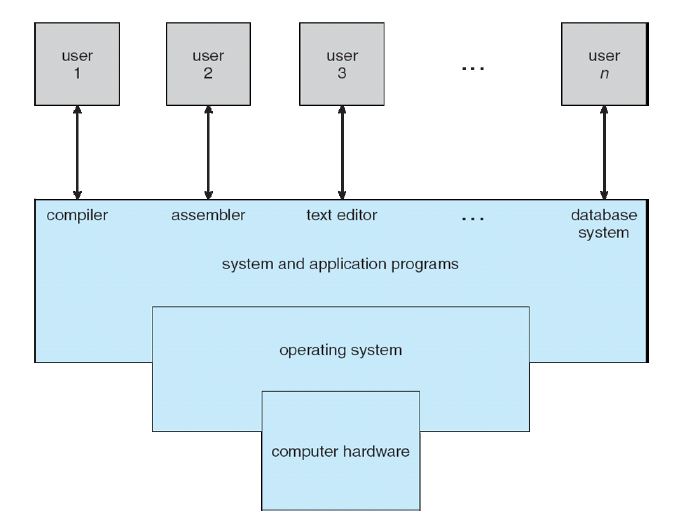
1.1 OS Definition
A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware.
Computer System Structure
1.1.1 User View
- ease of use
- Do not care about resource utilization!
1.1.2 System View
- resourse allocator
- control program
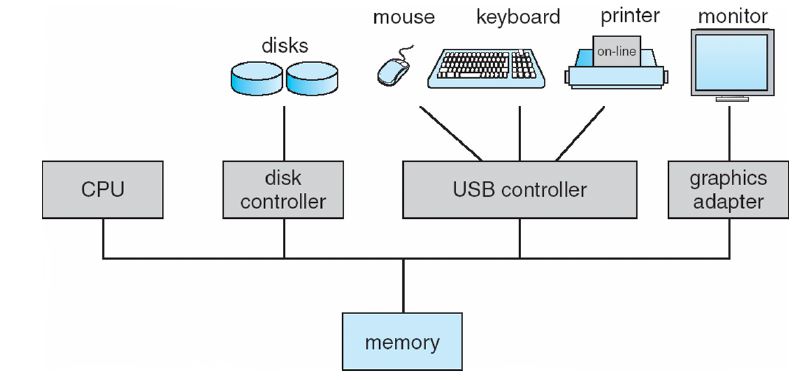
1.2 Computer-System Organization
bootstrap program:
- Typically stored in ROM or EPROM, generally known as firmware.
- Initializes all aspects of system.
- Loads operating system kernel and starts execution.
Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles. To ensure orderly access to the shared memory, a memory controller is provided whose function is to synchronize access to the memory.
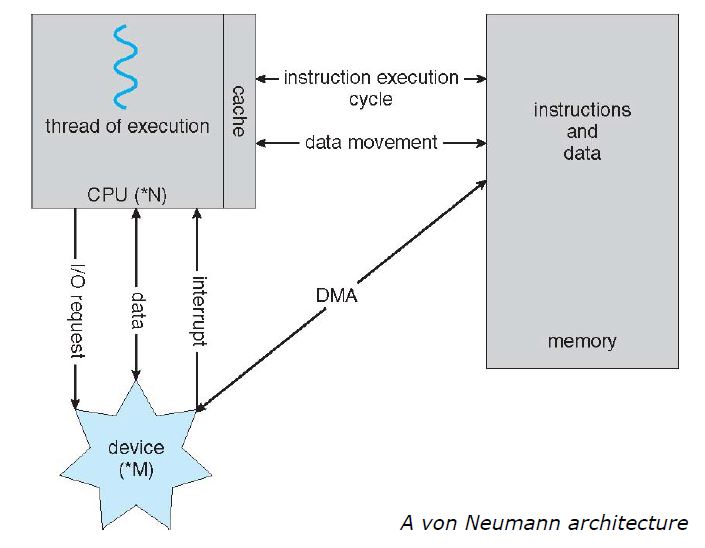
1.2.1 Interrupt
An operating system is interrupt driven. Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. More recent architectures store the return address on the system stack.
- Hardware interrupt: Caused by hardware interrupt signals, trigged by external events
- Software interrupt: Caused by privilege instructions, traps may trigger soft interrupts
- different type of interrupt
- polling
- vectored interrupt system
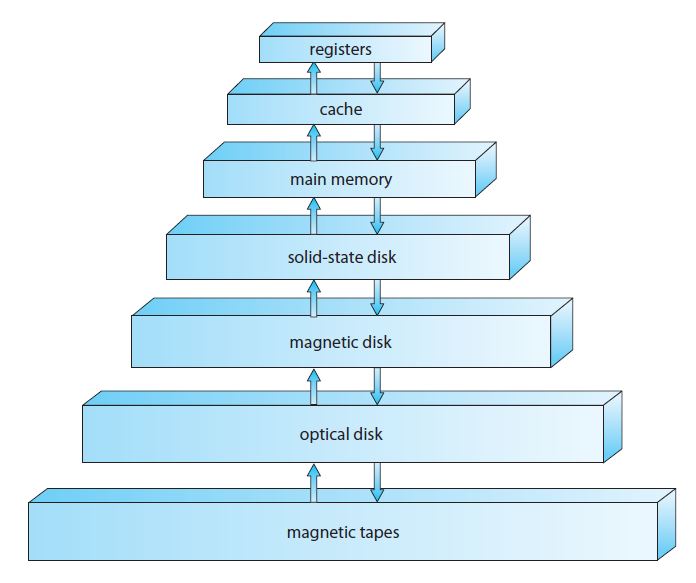
1.2.2 Storage Structure
1.2.3 I/O Structure
- Device Controller: maintains some local buffer storage and a set of special-purpose registers. It is responsible for moving the data between the peripheral devices that it controls and its local buffer storage.
- Device Driver: understands the device controller and presents a uniform interface to the device to the rest of the operating system. Device Controller informs the Device Driver via an interrupt that it has finished its operation.
- DMA
- Used for high-speed I/O devices able to transmit information at close to memory speeds
- Device controller transfers blocks of data from buffer storage directly to main memory without CPU intervention
- Only one interrupt is generated per block, rather than the one interrupt per byte
1.3 Computer-System Architecture
1.3.1 Single-Processor Systems
1.3.2 Multiprocessor Systems
Concurrent(并发) vs. Parallel(并行)
- Concurrent: concurrent execution can be accomplished on a single processor or by using time-sharing techniques, such as dividing programs into different tasks or threads of execution, or by using multiple processors.
- Parallel: use of multiple computers/processors to solve problems. Multiple programs simultaneously runs on several computers/processors.
Advantages:
- Increased throughput
- Economy of scale
- Increased reliability – graceful degradation or fault tolerance
asymmetric multiprocessing
Each processor is assigned a specific task.
symmetric multiprocessing(SMP)
Each processor performs all tasks within the operating system.
1.3.3 Clustered Systems
two or more individual computers (e.g. PC, servers, workstation), coupled together, connected via LAN, to provides high performance computing (HPC) and high reliability.
as one kind of popular distributed systems
1.4 Operating-System Structure
1.4.1 Multiprogramming
- Multiprogramming organizes jobs (code and data) so CPU always has one to execute
- A subset of total jobs in system is kept in memory
- One job selected and run via job scheduling
- When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job

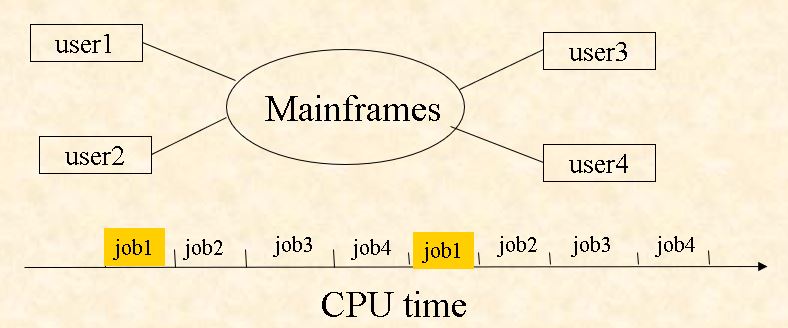
1.4.2 Time Sharing
Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing. CPU times are divided into timeslot (时间片),each user/process/job/task occupies one timeslot alternatively.
- Features:
- 多路性
- 交互性
- 独占性
1.5 Operating-System Operations
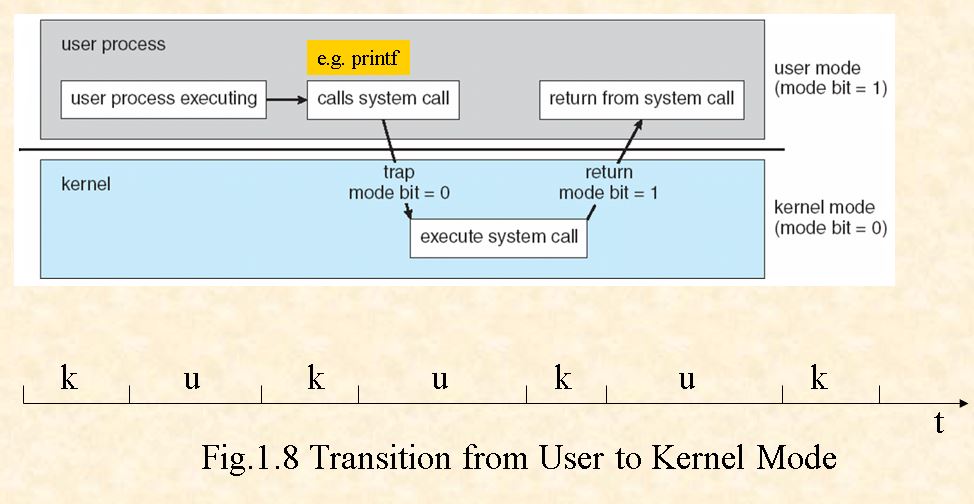
CPU modes: kernel mode, user mode
- Trap: a software-generated interrupt caused by an error or a request from user program that a OS service be performed. e.g System call.
1.5.1 Dual-mode operation and privileged instructions
- Mode bit: indicate the current operation mode
- 0: kernel/monitor/supervisor/system/privileged mode, in which OS and privileged instructions are running on CPU;
- 1:user mode, in which user programs are executing on CPU.
两种mode的切换方式:
notice: 1.if user programs in user mode attempt to execute privileged instructions, the hardware does not execute these instructions, but rather treats them as illegal operations. 2.User programs can execute system calls, a kind of special privileged instructions, to request the system to perform some designated task that only OS be permitted to do. A trap is generated in this process.
1.5.2 Timer
The timer is usually implemented by the fixed-rate clock and the counter
- clock ticker, 1ms clock, 10-bit counter, 1024ms clock
1.10 Distributed System
- Def: a form of information processing in which work is performed by separate computers linked through communication network.
- Advantages:
- resources sharing
- computation speed up – load sharing
- reliability
- communications
note: Required networking infrastructure: Local area networks (LAN) or Wide area networks (WAN, WWW)
- features
- task allocation
- communications via networks — allowing different processors on different computers to exchange information
- process synchronization
- load sharing
- distributed file systems — files sharing across the network
1.11 Specific-Purpose Systems
- Real-Time System
- Embedded System
1.12 Computing Environments
Traditional computing
Client-Server Computing
Peer-to-Peer Computing
Web-Based Computing
Chapter 2: OS Structure
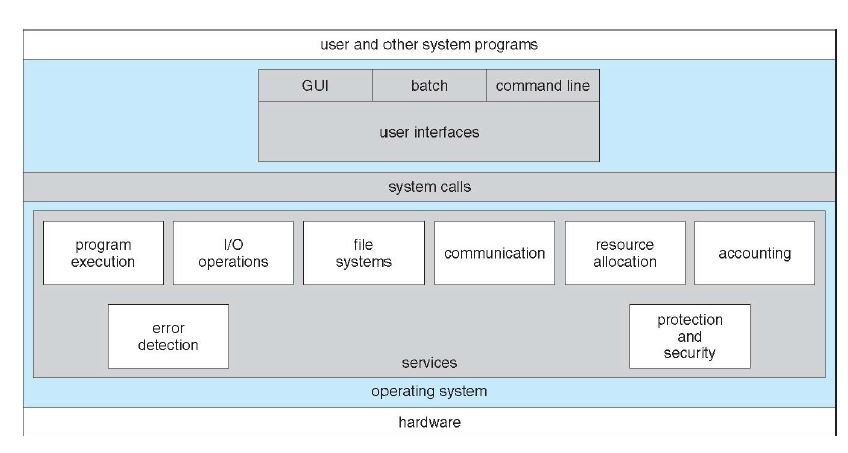
2.1 OS Services
2.1.1 Definition
Operating systems provide an environment for execution of programs and services to programs and users.
2.1.2 A view of Services
The following 6 services are user-oriented services.
- User Interfaces
- command-line interface
- batch interface (off-line interface, 作业控制接口)
- graphical user interface (GUI)
- program execution
- system capability to load a program into memory and to run it
- I/O operations
- since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O
- file-system manipulation
- capability to read, write, create and delete files
- communications
- exchange of information between processes executing either on the same computer or on different systems tied together by a network
- error detection
- ensure correct computing by detecting errors in the CPU and memory hardware, in I/O devices or in user programs
The following 3 services are for ensuring efficient system operations.
- resource allocation
- allocating resources to multiple users or multiple jobs running at the same time
- accounting
- keep track of and record which users use how much and what kinds of computer resources for account billing or for accumulating usage statistics
- protection and security
- ensuring that all access to system resources is controlled
2.2 User Operating-System Interfaces
- Command interpreter
- Shells
- GUI