Recursive Neural Network
I. RNN Structure Overview
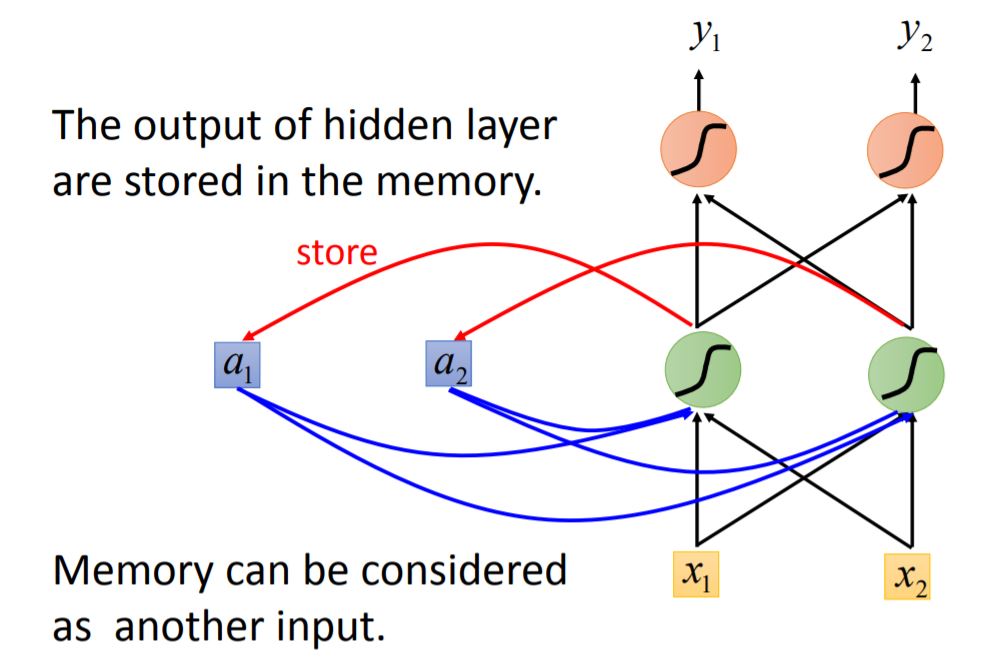
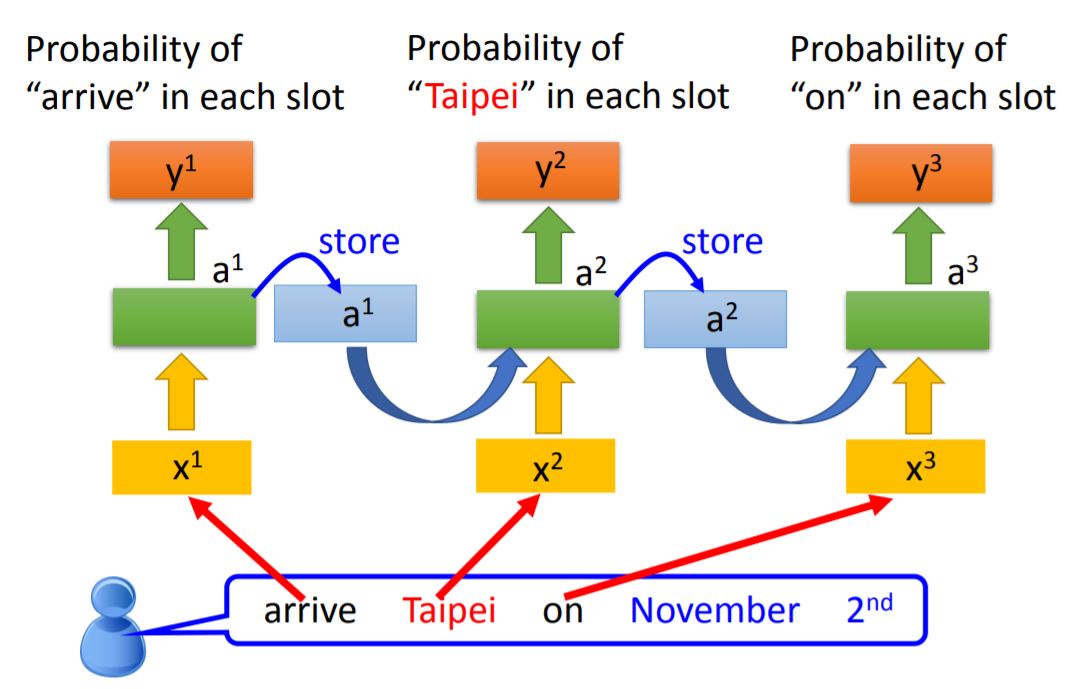
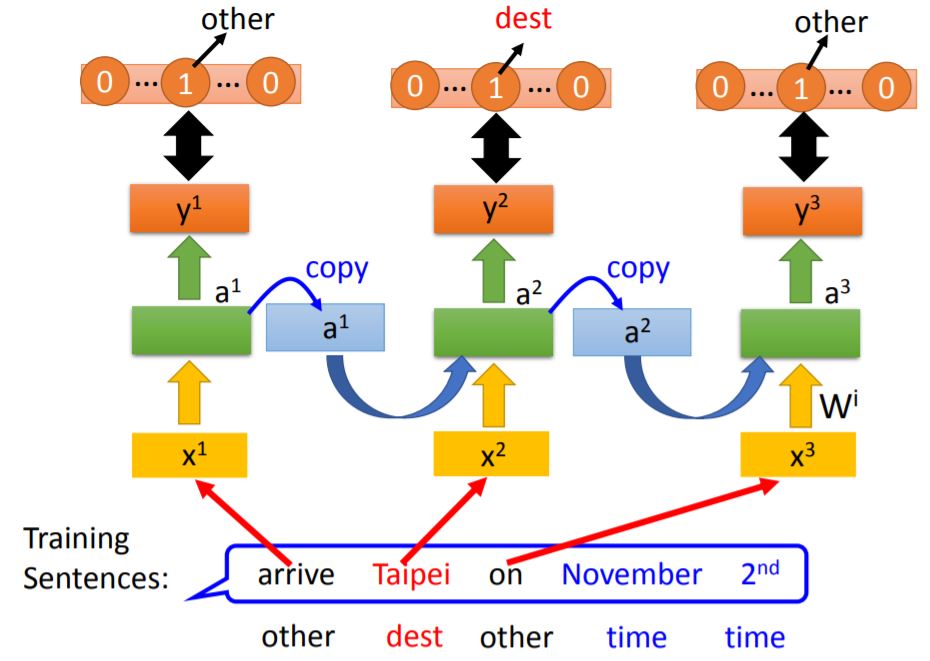
The input is a sequence of vectors.
note: Changing the input sequence order will change the output
We use the same neural network to train, each color in NN means the same weight. When the values stored in the memory is different, the output will also be different.
II. Types of RNN
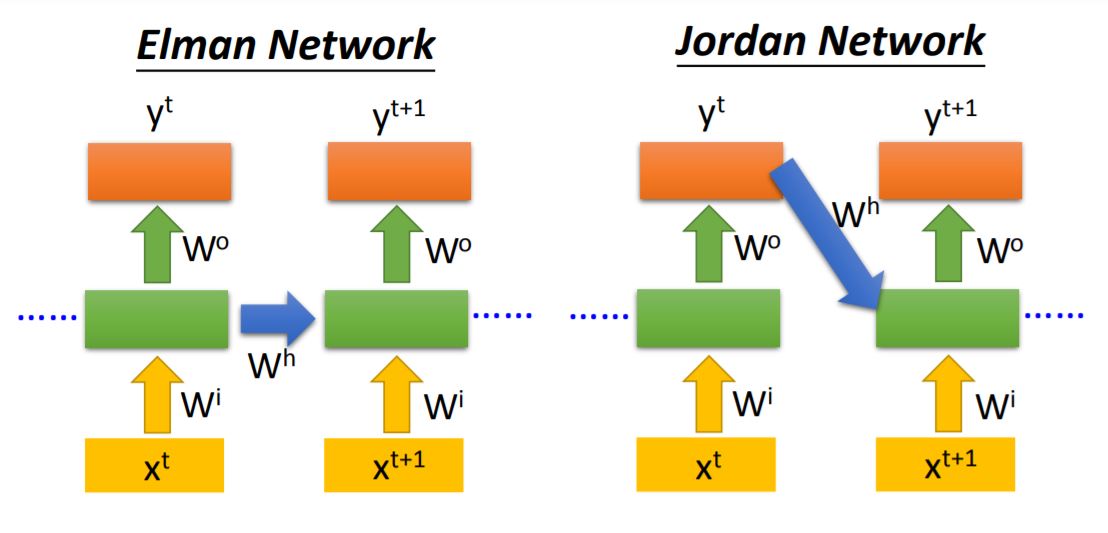
Elman’s memory restore the values of hidden layer output, and Jordan’s memory restore the values of output. Usually Jordan network have better performance because output y has target.
Bidirectional RNN
Using bidirectional RNN can get the information from the context. For example, for the hidden layer output $y^{t+1}$, its value is determined by not only $x^t$ and $x^{t+1}$ but also $x^{t+1}$ and $x^{t+2}$.
III. *Long Short-term Memory (LSTM)
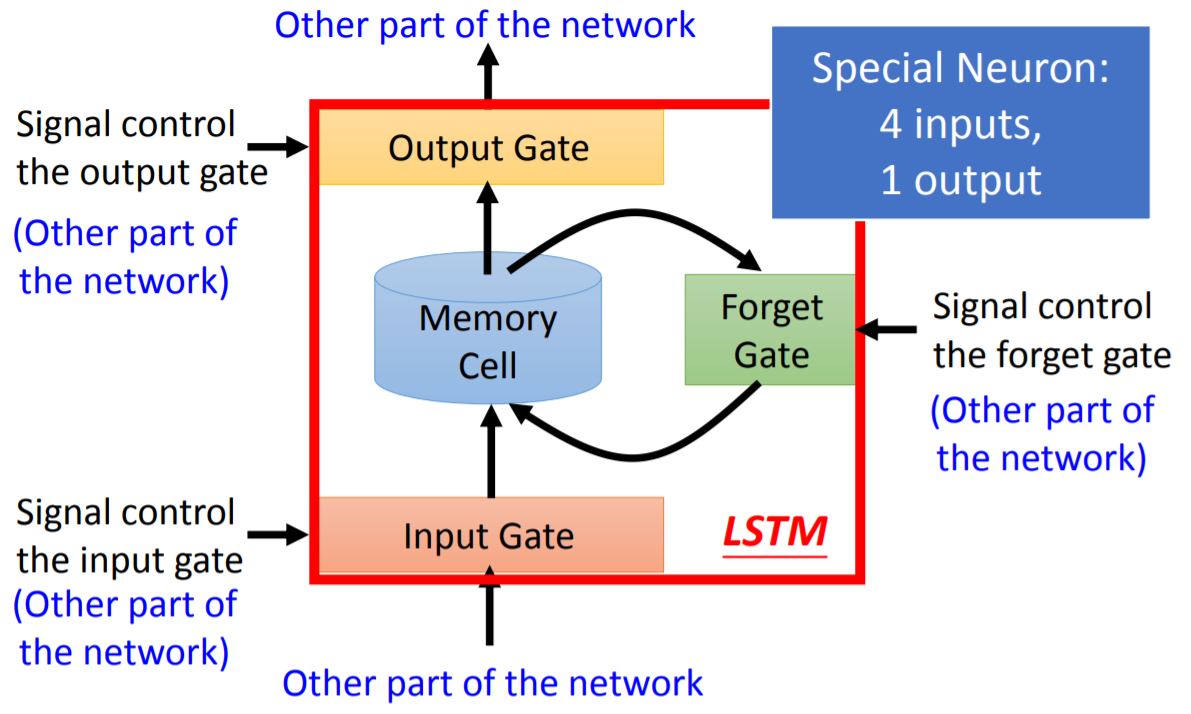
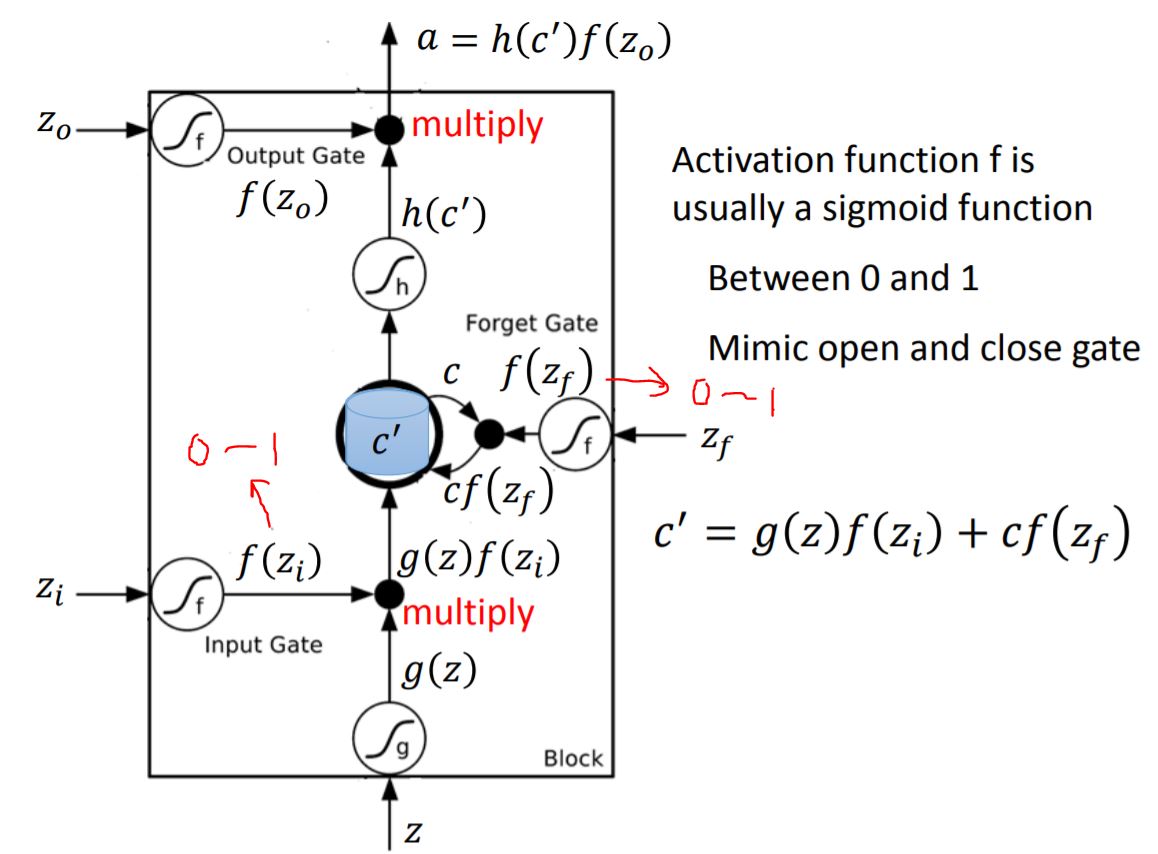
1. LSTM Overview
Input gate: Decide whether the input can be written in memory cell;
Output gate: Decide whether the output of memory cell can be sent to other part of the network;
Forget gate: Decide whether the content in memory cell should be erased.
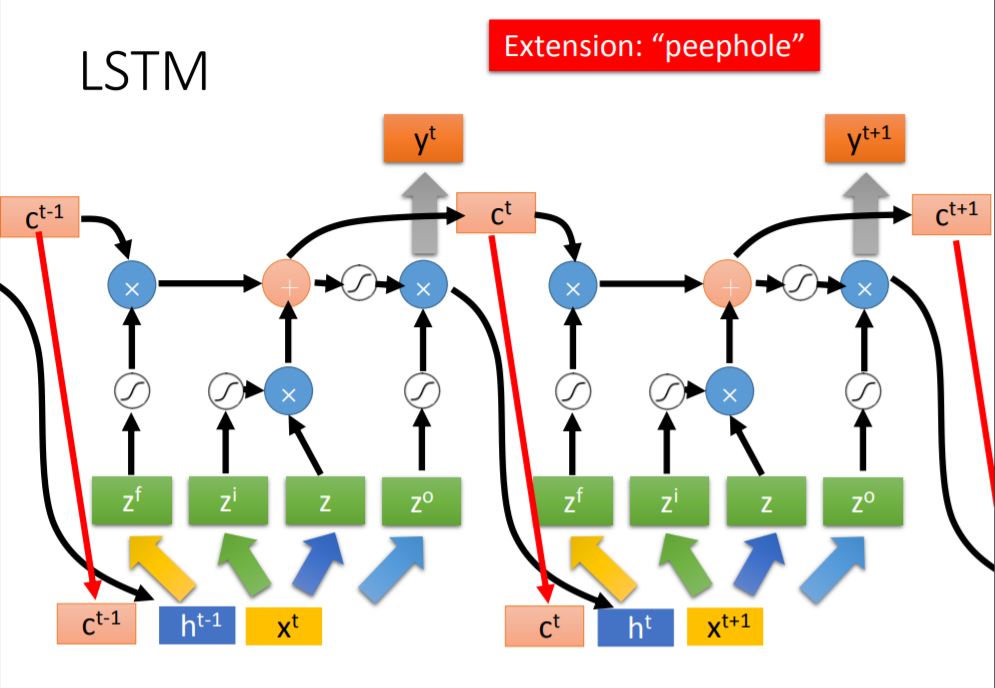
2. Detailed process
3. Example
此处强烈建议看一下PPT中的LSTM讲解: Every scalar is determined by input vector(例子中是三维) through linear transform, which means every input vector multiply the corresponding weight and add the bias. All the weight and bias are trained by trainig data through GD.
4. LSTM’s parameter
LSTM的每一块相当于原neural network的神经元,可以直接替换。LSTM的参数量为feed-forward NN的参数量的4倍。
5. LSTM Model
In fact, you could use model in Keras such as “LSTM”, “GRU”(simplified LSTM) and “SimpleRNN”.
IV. RNN
1. Loss Function
The cross-entropy between RNN output and reference vector for every time slot.
Reference vector就是每一个单词所对应的reference组成的向量。
2. Learning
Method: Backpropogation through time (BPTT)
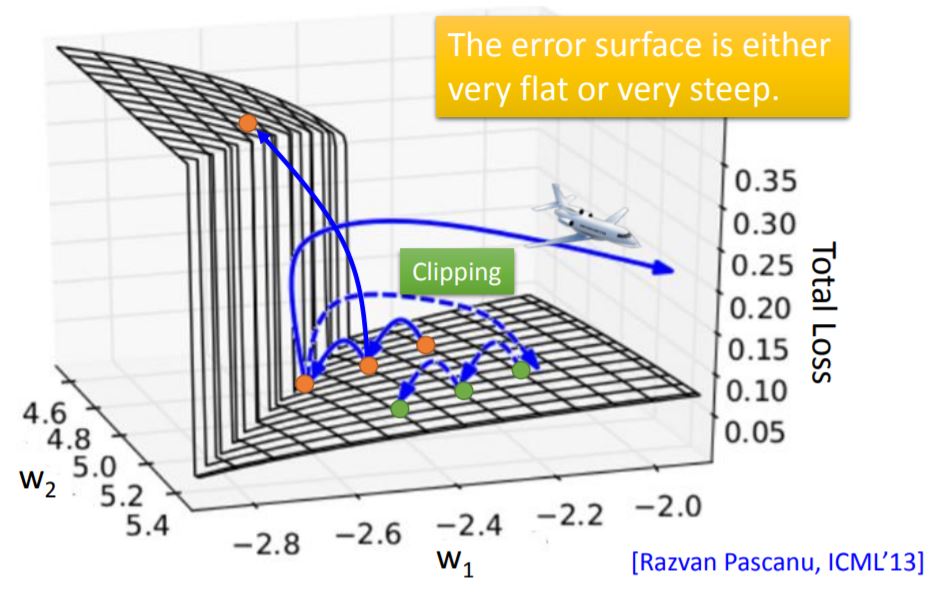
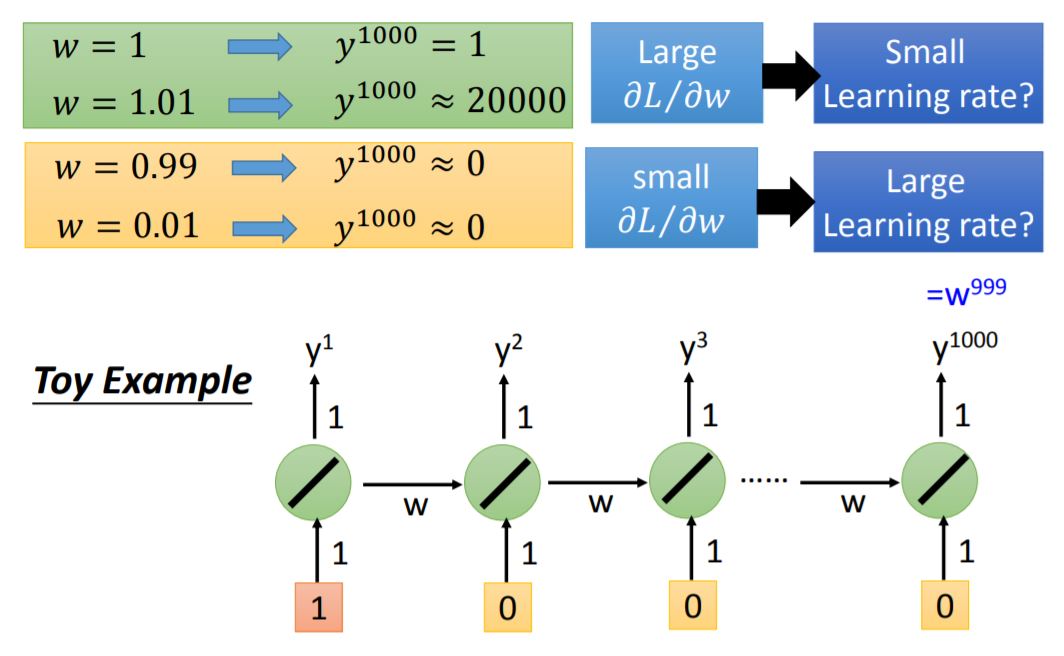
However, RNN-based network is not always easy to learn. The error surface is either very flat or very steep. When you step into a point whose gradient is relatively large and your learning rate is also large, your learning step will make a really huge move so that the program will tell you segmentation fault.
One way to avoid this circumstance is to use Cliping, which means to set a threshold of gradient and every move can not larger than the threshold.
The reason for this rough error surface is shown as below:
3. Helpful Techniques
- RNN vs LSTM
LSTM can deal with gradient vanishing(not gradient explore).
- LSTM: Memory and input are added and storedin memory unless forget gate is closed. RNN: Every time memory will be formated.
- The influence never disappears unless forget gate is closed.
此处老师说有国际大厂面试里考过哦!
Note: Gate Recurrent Unit(GRU) is simpler than LSTM for it has only two gate. 它将 input gate 和 forget gate 进行了联动。
Other techniques:
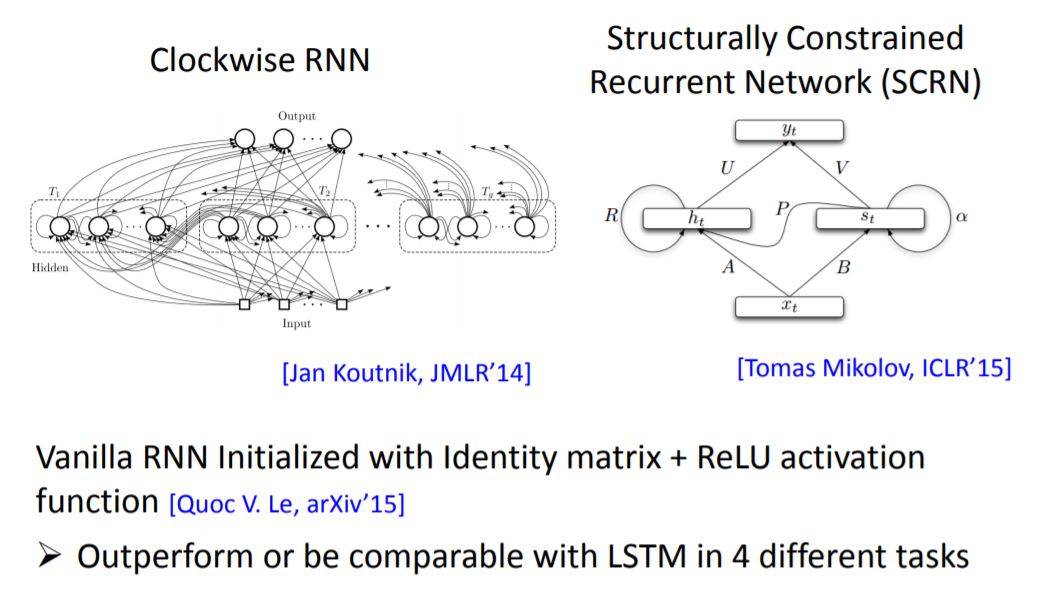
此处老师讲述了Hinton的一篇论文,用一般training的方法,initialize的weight是random的话,sigmoid的效果要好于ReLu;他用indentity matrix来initialize weight,这样使用ReLu作为Activation函数则可以显著提高效果。利用这种方法的RNN在效果上吊打LSTM。非常的玄学
4. More Application
- Many to one: Input is a vector sequence, but output is only one vector
- Many to many: Both input and output are both sequences, but the output is shorter.
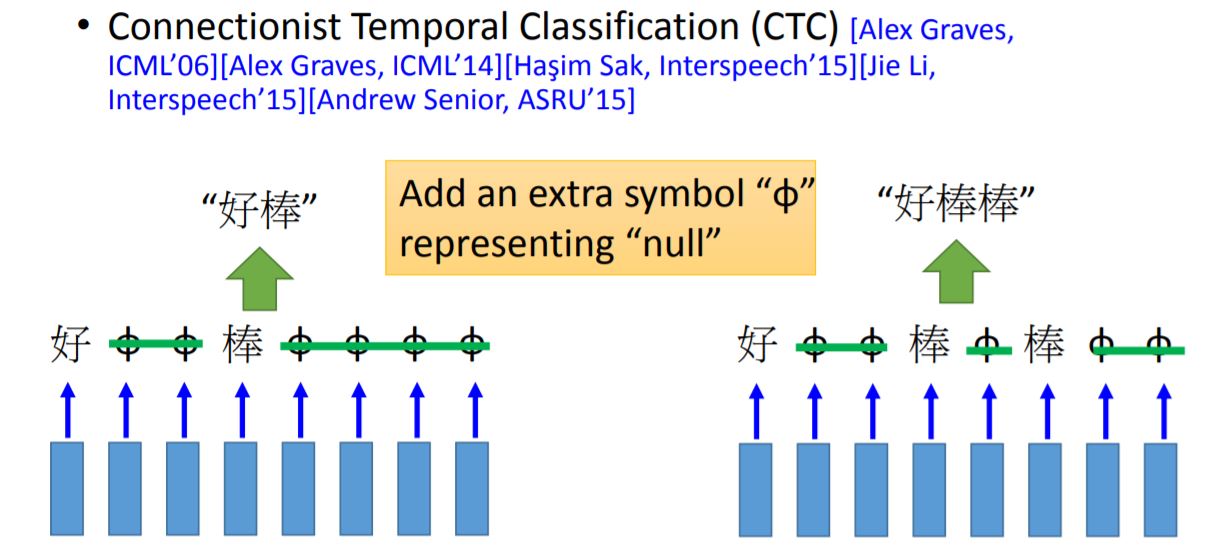
CTC
Sequence to sequence learning 有一篇论文讲到可以直接将某种语言的语音信号作为输入,得到另一种语言文字形式的输出,并发现其有可行性。
- Seq2seq Auto Encoder(没听懂)
V. Attention-based Model
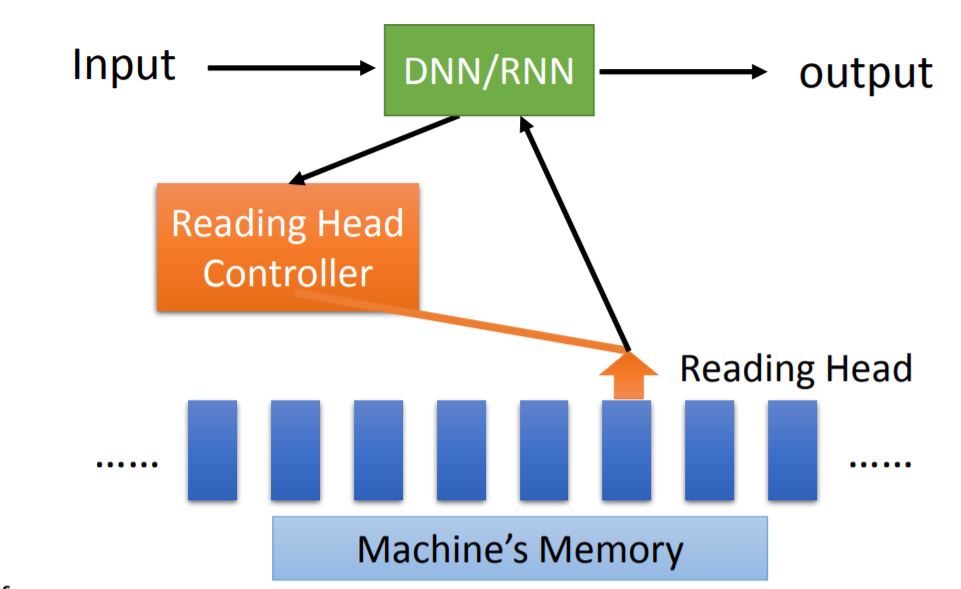
1. Model Overview
其中的DNN/RNN类似于计算机中的CPU概念。
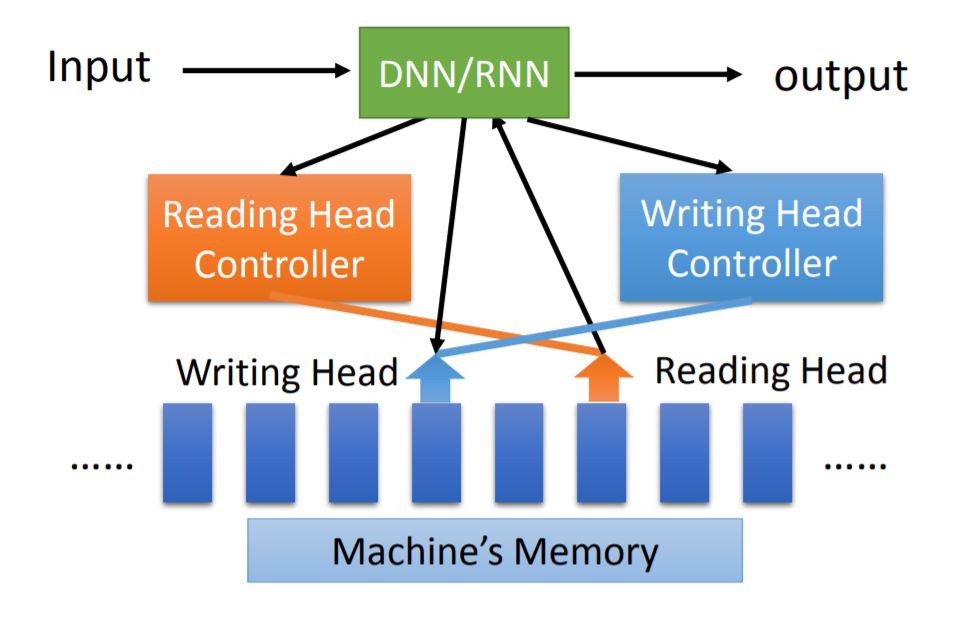
2. Model version 2
Neural Turing Machine: