Convolutional Neural Network
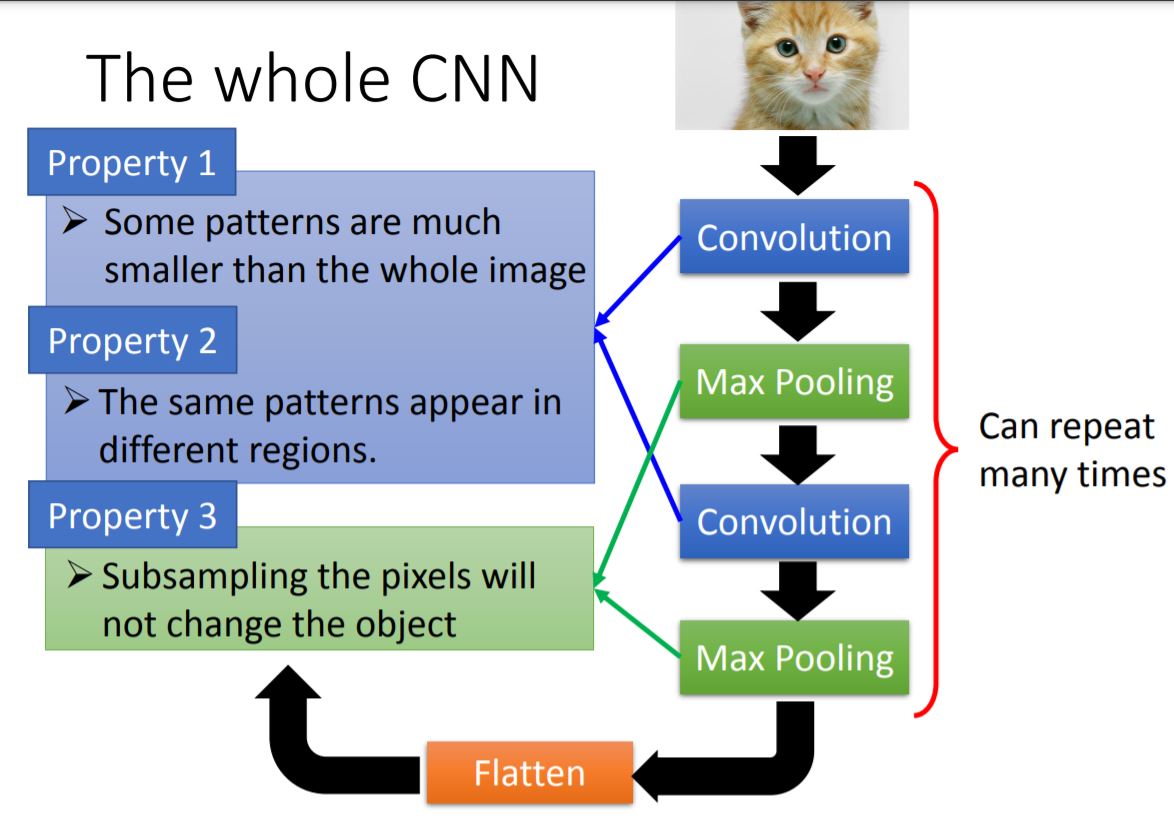
I. CNN Structure Overview
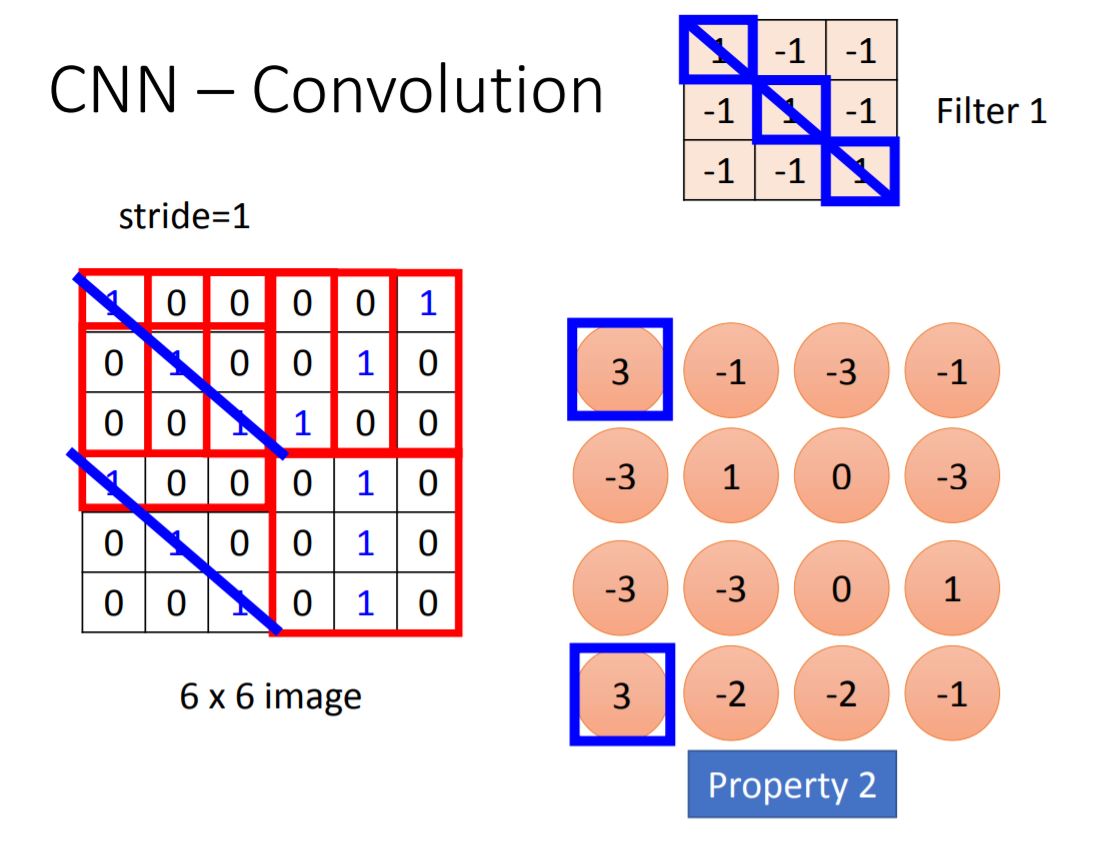
II. Convolution
Note: 1.Every elements in filter are the network parameter to be learned. 2.Stride means each step you walk from previous position. 3.The size of filter is decided by programmer.
From the picture we could know the largest values of Feature Map means there has a feature. Then we do the same process for every filter and generate more Feature Map.
If we deal with colorful image, we will use Filter Cube instead of matrix.
Then there is a question: What is the relationship between Convolution operator and Fully Connected ?
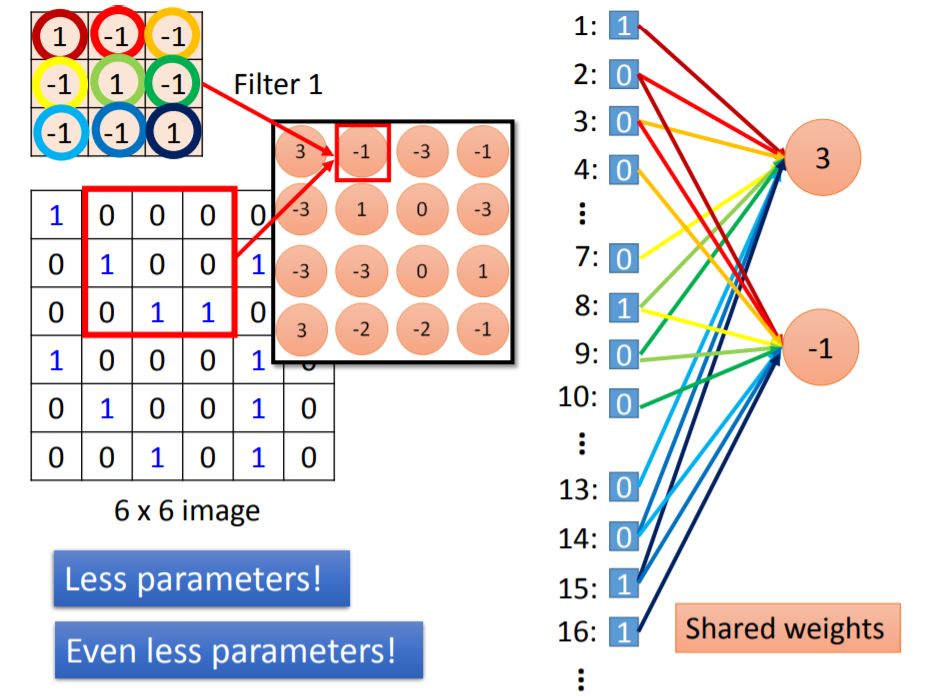
这里请注意每一个输出对应连接的weight是共享的(也就是一致的),从图里看出共享weight的颜色是相同的。
III. Max Pooling
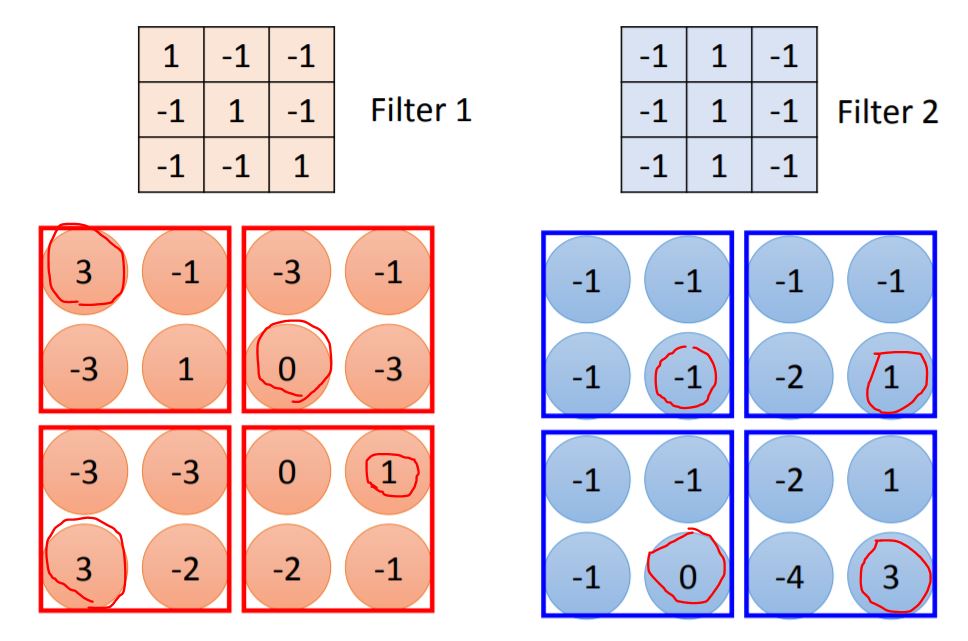
Note: Each filter is a channel. The number of the channel is the number of filters.
在这里着重强调一下,每一次进行重复卷积池化的时候,filter是不一样的。第一次卷积池化时filter是二维向量,但到了第二次卷积池化时,feature map作为新的输入已然是cube的形状,此时并不会需要更多数量的二维向量filter,而是会使用cube形状的filter进行内积操作。
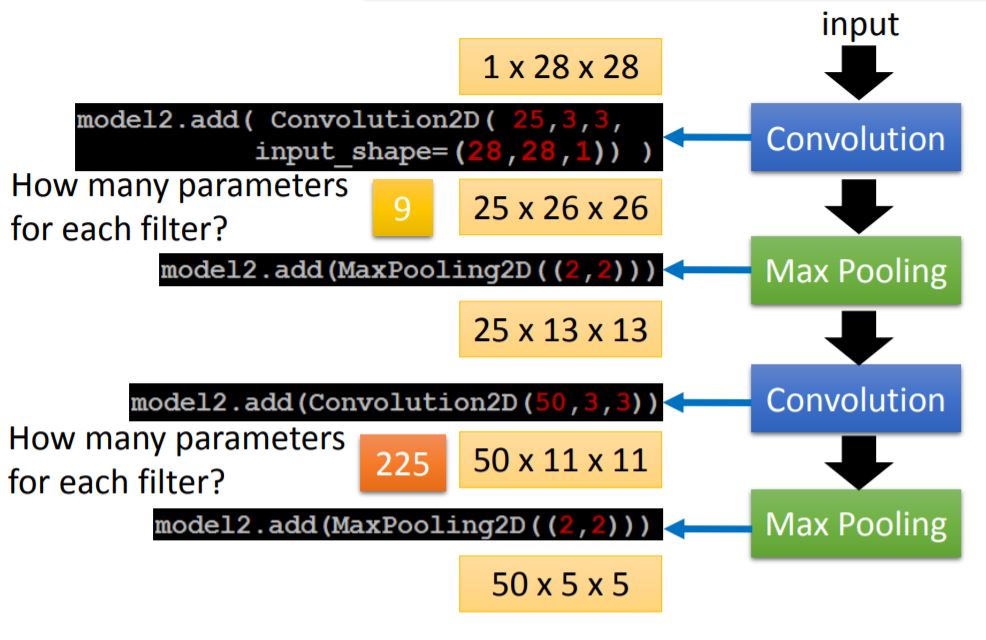
IV. One Example
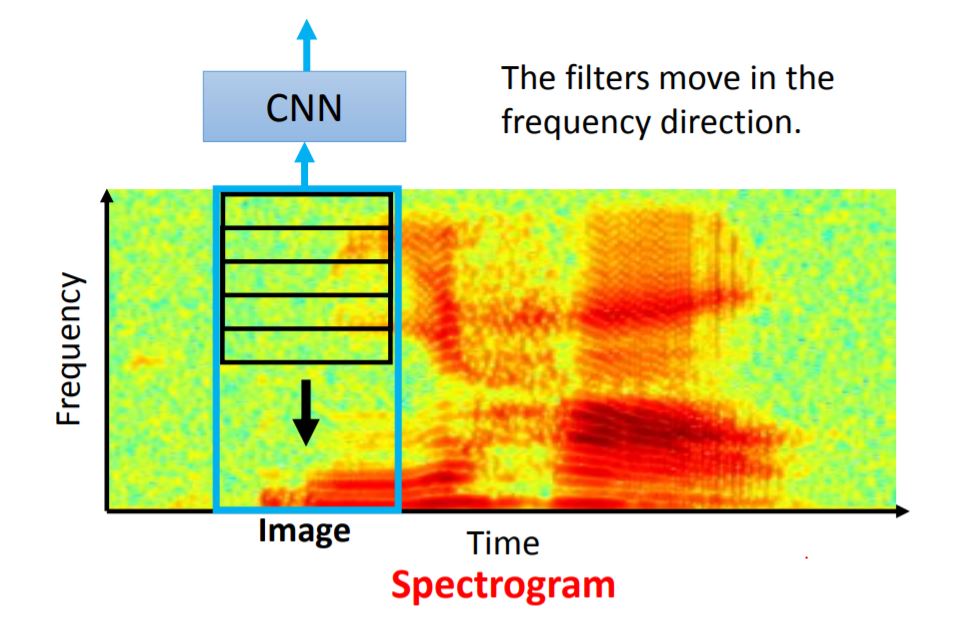
More Application
对于这种Spectrogram的图像识别而言,运用CNN的技术可以实现对某些task的识别。由于在CNN之后会接上LSTM等架构,导致在CNN模块中对时间域的提取并不会提高模型的性能,所以一般filter只会在频域中进行卷积。