Database System Lecture Note 4
Chapter 12 Query Processing
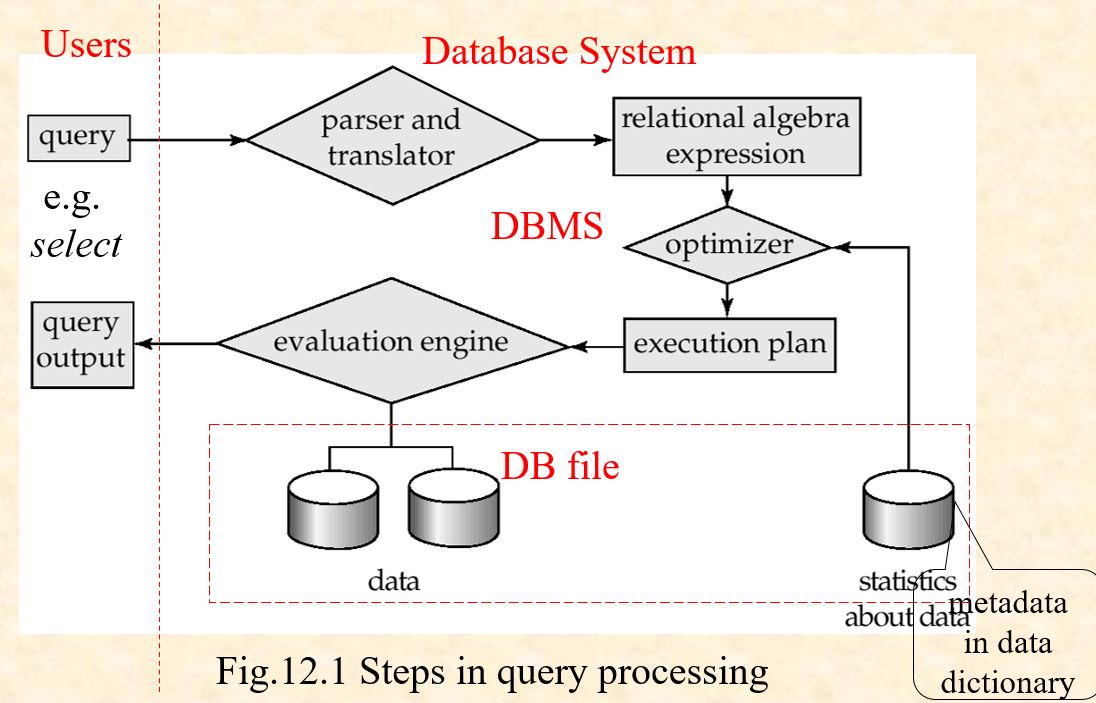
12.1 Overview
12.2 Measures of Query Cost
Disk access is the predominant cost. Use the number of block transfered from disk and the number of seeks as the cost measures.
12.3 Selection Operation
- Types of query conditions (查询条件类型)
- equality(等值), e.g.salary = 100
- range (范围), e.g. salary between 50 and 400
- comparison (比较), e.g. salary >300
NOTE: B+索引可以使用全部查询类型,而Hash索引只能等值查询。
- Several file scan algorithms
- linear search/scan – A1 无索引、乱序:扫描全部blocks,才能找到全部满足查询条件的数据。 Cost estimate = $b_r$ block transfers + 1 seek
- selections using indices – A2, A3, A4
- A2 主索引:Cost = $(h_i + 1) \times (t_T + t_S)$
- A3 聚集索引不唯一:Cost = $h_i \times (t_T + t_S) + t_S + t_T\times b$
- A4 非聚集索引不唯一:Cost = $(h_i + n) \times (t_T + t_S)$
- selections involving comparisons – A5, A6
- A5: 主索引,找叶子节点
- A6: 辅索引,找叶子节点所指向的记录
- complex selections – A7, A8, A9, A10
12.4 Sorting
merge sort,排序、去重
12.5 Join Operation
nested-loop join, merge join, hash join
12.6 Other Operations
project, distinct(去重), order by, outer join, aggregation
12.7 Evaluation of Expressions
- Materialization serial evaluating
- start from the lowest-level, i.e. at the bottom of the tree, evaluate one operation at a time.
- the results of each evaluation (i.e. intermediate computing results) are stored in temporal relations on the disk for subsequent evaluation .
- Pipelined parallel evaluating evaluate several operations simultaneously in a pipeline, with the results of one operation passed to the next, without the need to store temporary relations in disk