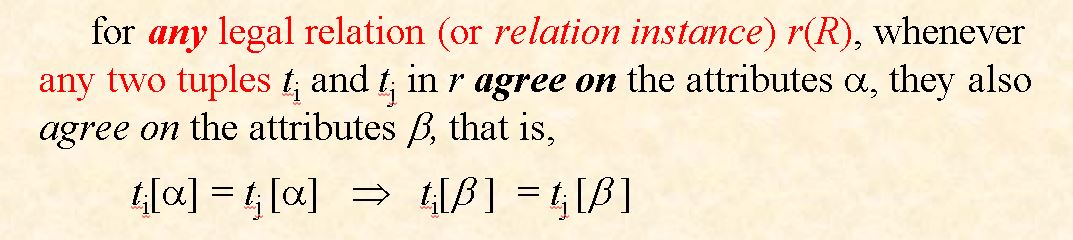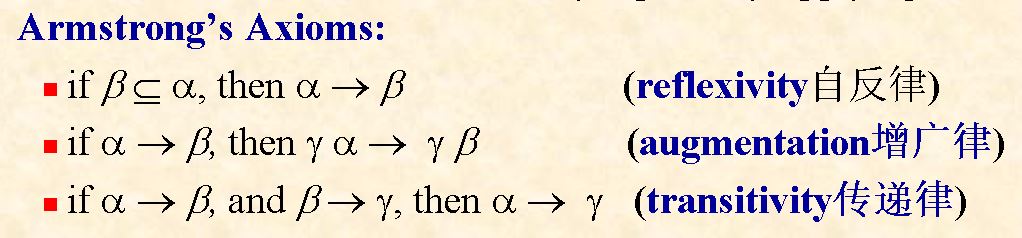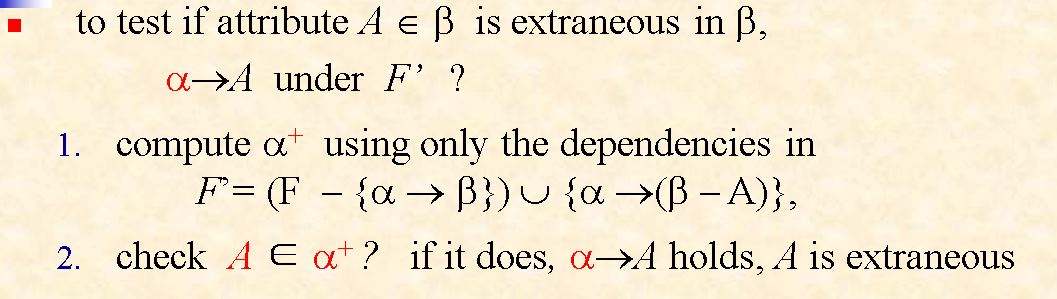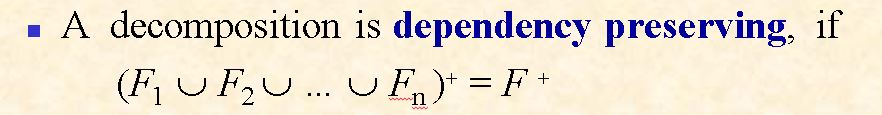Database System Lecture Note 2
Chapter 7 Database Design and E-R Model
7.2 Concepts
- Entity sets
- Relationship sets 对于多元联系$\Rightarrow$二元联系$\Rightarrow$关系表
- Attribute
7.3 Constraints
- Mapping Cardinalities
- one to one
- one to many
- many to one
- many to many
- Keys
- superkey
- candidate key
- primary key
Chapter 8 Schema Normalization
核心思想:将large schemas decompose to smaller schema. 建立functional dependency, 并利用两表查询的的方式进行查询(此处详见第7章)。 在第7章通过将E-R图进行转换,得到面向特定的初始关系模式集,这些关系模式集可能存在多种数据依赖关系:
- Functional Dependencies
- Multivalued Dependencies
- Join Dependencies (略)
如果直接根据初始关系模式构造DBS,由于初始关系模式中数据依赖关系的存在,可能会违反DB的完整性约束
- pitfalls:插入、更新、删除问题
因此,对初始关系模式集,需要根据关系规范化理论,在保证关系模式的
- lossless join
- dependency preservation
步骤大致为:
- 根据函数依赖的Armstrong’s 公理系统 ( §8.4.1 )和多值依赖 的公理系统 ,从初始关系模式集中已知的函数依赖和多值依赖出发,推导出初始关系模式集中所有的函数依赖(§8.4)和多值依赖(不作要求)
- 模式分解算法,对其进行(等价)分解和变换,将其转换为各种范式形式。
8.2 Atomic Domains and First Normal Form
Atomic Domains: its elements are considered to be indivisible units. 反例:集合(非原子域)、复合属性等
First Normal Form: A relational schema R is in first normal form if the domains of all attributes of R are atomic
8.3 Decomposition Using Functional Dependencies
8.3.1 Functional Dependencies
Def1: Functional dependency(FD) holds on R
Keys in relational schema can be defined in terms of FD
- K is a superkey for relation schema R, if and only if $k \rightarrow R$
- K is a candidate key for R, if and only if
- $k \rightarrow R$,
- and for no $\alpha \subset K, \alpha \rightarrow R$
Def2: (A particular relation instance) r(R) satisfy FD, or FD is satisfied by r(R).
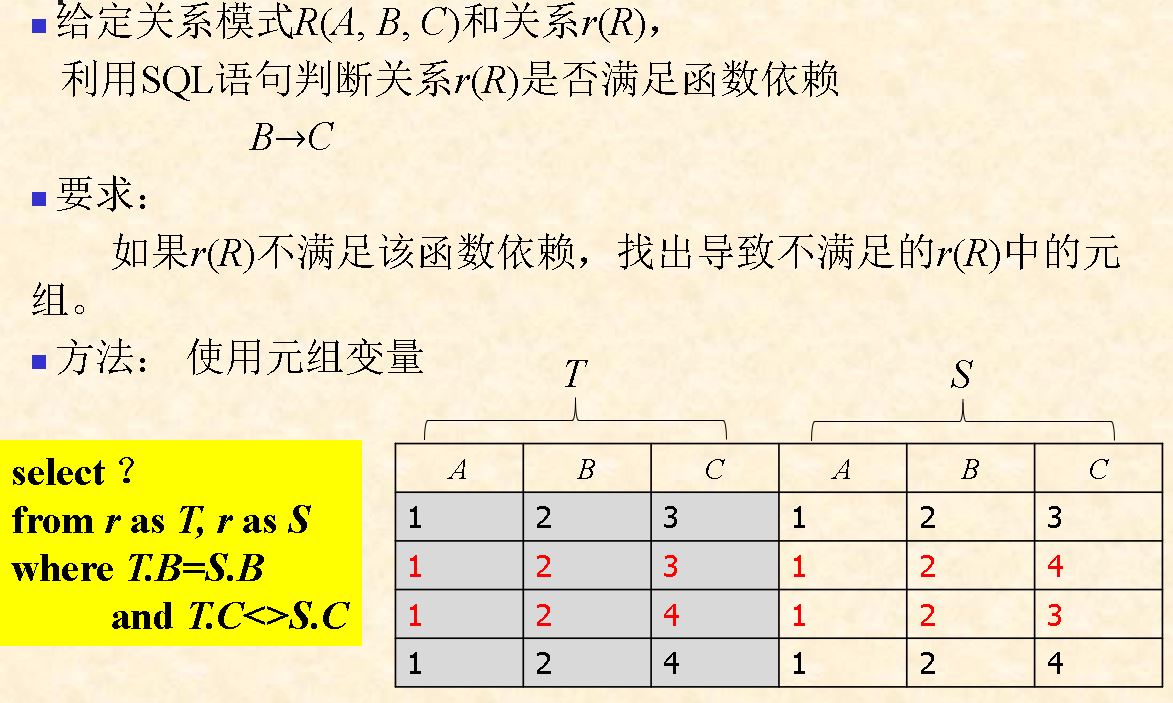
How to guarantee the FD in DBS? answer:用SQL检查2个属性之间的FD
FD holds on R: 整体要求,定义在R的属性间的语义约束 FD is satisfied by r(R): 部分满足 意思是对于关系R而言,即使它的关系实例r(R)满足某些FD,也不能代表整个关系R就满足该FD!可能只是该关系实例的数据凑巧满足而已。(容易出判断题考察)
Trivial FD: 所有关系实例均满足FD,大多是右边属性包含于左边
Transitive dependency (传递函数依赖)
Partial dependency (部分函数依赖) 即对于$\alpha \rightarrow \beta$中,$\alpha$含有冗余项。
Closure of FD The set of all functional dependencies logically implied by F is the closure of F, denoted as $F^+$.
8.3.2 Boyce-Codd Normal Form
- Def:
每一个FD需要满足其中之一的性质
- Decomposing a Schema into BCNF:
相当于外键关联
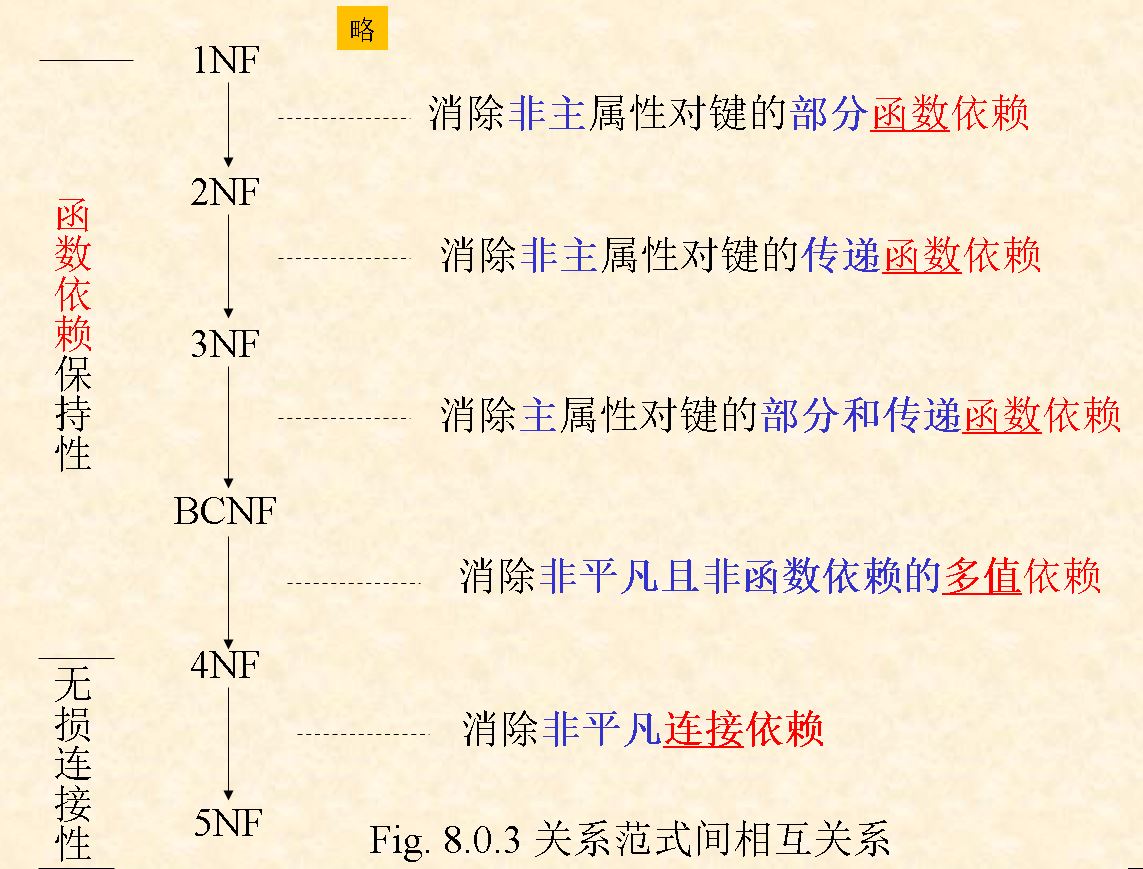
ATTENTION:BCNF 并不能保持函数依赖,所以需要考虑上一级的3NF
8.3.4 Third Normal Form
Def:在BCNF的定义中添加该性质
性质:(必要条件)
- R is also in 2NF
- 不存在非主属性对候选键的部分和传递依赖,i.e.每一个非主属性都不传递依赖于R的任何候选键
重要!!!!
检测关系模式是否满足函数依赖的方法
8.4 Functional-Dependency Theory
8.4.1 Closure of a Set of FD
定义在上面已经给出
Logically implied: Given a schema R, a functional dependency f on R is logically implied by a set of FD F on R , if every instance r(R) that satisfies F also satisfies f. 简而言之,某个函数依赖f可以被F这个集合推出来
Armstrong’s Axioms
8.4.2 Closure of Attribute Sets
Def: An attribute B is functionally determined by $\alpha$ if $\alpha \rightarrow B$.
Def
注意该集合是有限的
若通过某些属性推出R,说明其为superkey,接下来判断其是否是candidate key.
Uses of Attribute Closure
这里的第二种用途是第二种测试函数依赖的方法,相比SQL方法更为简单方便。
等价的概念
8.4.3 Canonical Cover
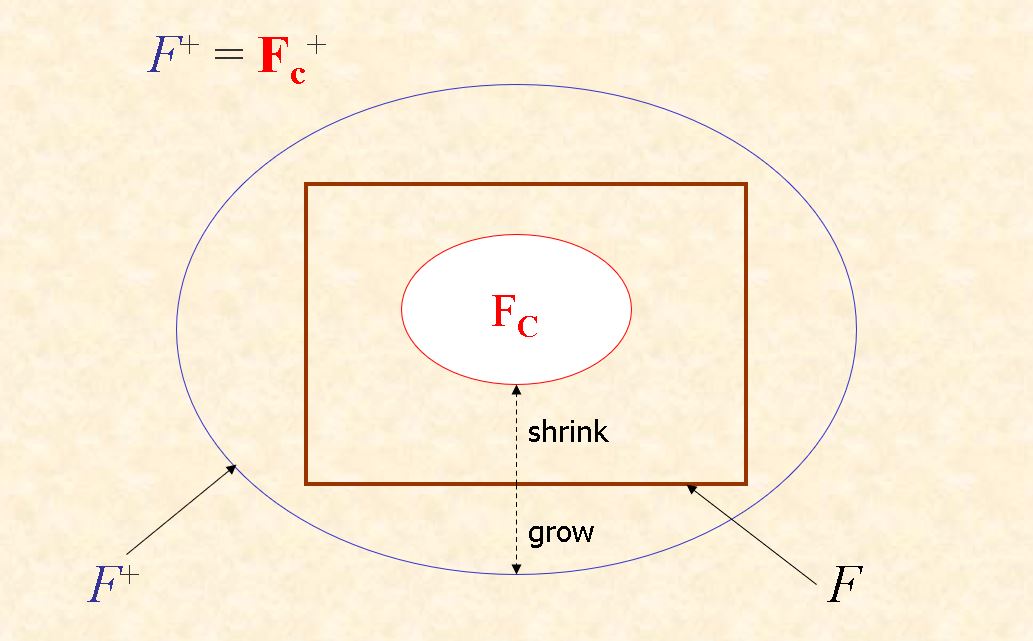
用于去除FD set中函数依赖的左右两端的冗余项。正则覆盖是最小的与F等价的函数依赖集合,记作$F^+ = F^+_c$。
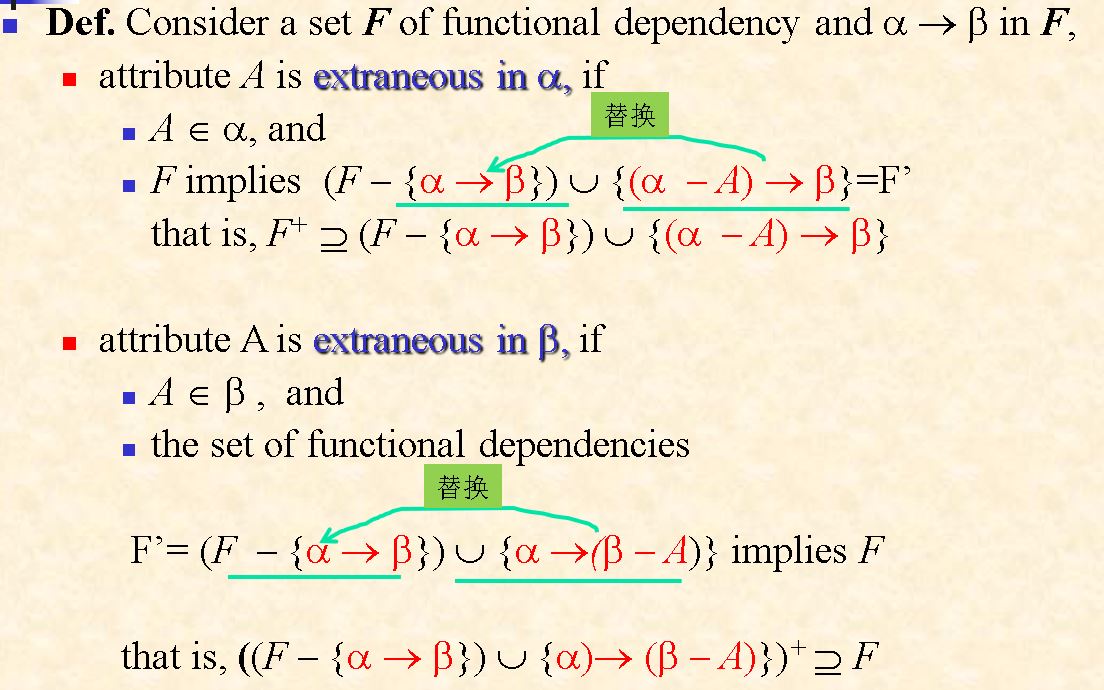
Extraneous Attributes
两种情况的解决问题方案
- 当冗余元素在左边出现的时候
在原有函数依赖下,求属性闭包,用于判断冗余属性
- 当冗余元素在右边出现的时候
在新的函数依赖之下求属性闭包
- 当冗余元素在左边出现的时候
在原有函数依赖下,求属性闭包,用于判断冗余属性
A canonical cover for F is a set of dependencies Fc such that 所有函数依赖的左边不会相同,这种判断方法来源于求出canonical cover的算法。
Compute a canonical cover
8.4.4 Lossless-join Decomposition

8.4.5 Dependency Preserving
Restriction of F to Ri
Dependency Preserving 子模式FD成立可以推出原模式FD成立,用于测试dependency preserving。
注意以下这种情况:

$A|F_1$ 代表在函数依赖集$F_1$下A可以推出的attributes sets
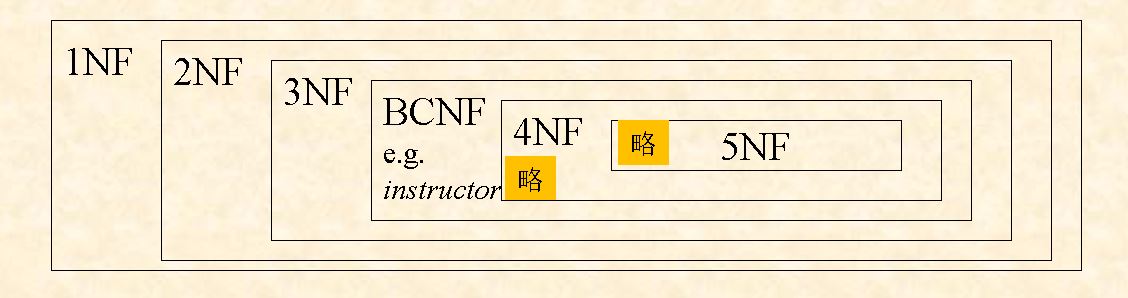
总结:范式之间的关系
Second Normal Form
相当于第二范式的每一个函数依赖的左边不能出现可分的超键。
Third Noramal Form
BCNF
8.5 Algorithms for Decomposition
8.5.1 BCNF Decomposition
算法步骤如下:
- 找出non-BCNF子模式Ri,进一步分解;
- 求出F在Ri上的投影和该关系的候选键;
- Ri是non-BCNF的原因在于$\alpha \rightarrow \beta$中$\alpha$并不是superkey。
- 将Ri中分解成2部分,公共属性$\alpha$,其中$\alpha\rightarrow \beta$单独组成BCNF模式
Note: to determine whether or not Ri is in BCNF, the restriction of F to Ri and the candidate keys of Ri should be computed !!! 在分解出新的Ri以后,首先求出F在Ri上的投影和该关系的候选键,然后再用算法进行判断
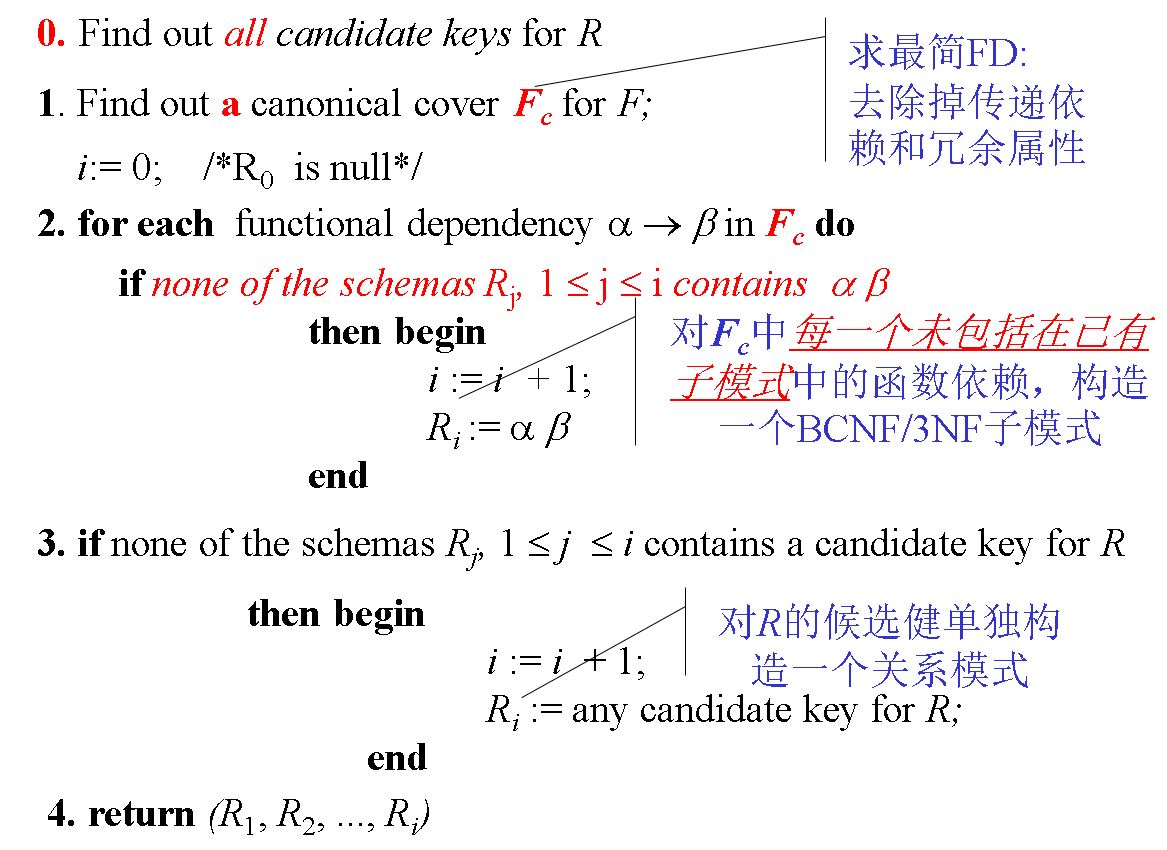
8.5.2 3NF Decomposition
- Functional dependencies can be checked on individual relations without computing a join.
- There is always a lossless-join, dependency-preserving decomposition into 3NF.
Note:
- All candidate keys should be founded out.
- Only one Fc should be computed at first
如何用SQL语句表达、测试函数依赖?
- 先分组再count,但无法找出不符合函数依赖的元组
select b
from r
group by b
having count(distinct c) > 1
- 利用两表查询的方式
select ?
from r as T, r as S
where T.B == S.B and T.C <> S.C
8.5.3 Computing of Candidate Keys
将R的所有属性分为四类: L类:仅出现在F中函数依赖左部的属性 R类:仅出现在F中函数依赖右部的属性 N类:在F中函数依赖左右两边均未出现的属性(该属性一定为候选键) LR类:在F中函数依赖左右两边均出现的属性
X_set代表L、N类,Y_set代表LR类
本章练习题:
- 给定关系表r(R)和若干函数依赖,判断r是否满足函数依赖 运用SQL语句
- 判断关于函数依赖的一些公式是否成立: Armstrong Axiom
- 求候选键
- 求属性闭包
- 求函数依赖集F的最小正则集
- 给定关系模式R和定义在R上的函数依赖集F,判断R属于第几范式
- 判断一个模式分解是否为无损连接、函数依赖保持
- 3NF、BCNF范式分解