Database System Lecture Note 1
Chapter 1 Introduction
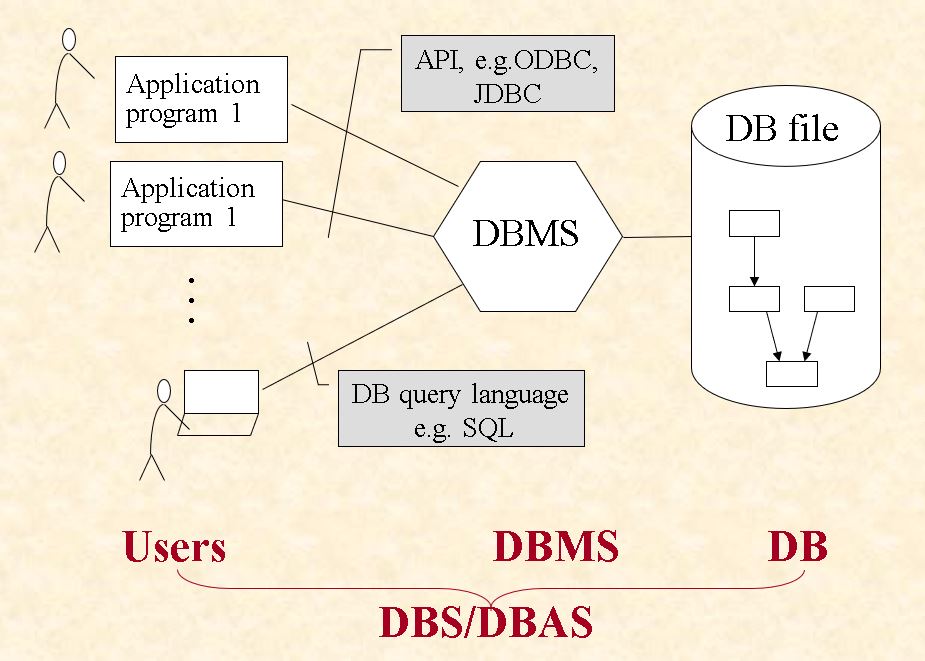
1.1 DB, DBMS, DBS, DBAS
- DB:
- a collection of interrelated data
- stored in systems as files
- DBMS:
- a set of programs to access the data in DB
- DBS: users + DBMS + DB
1.2 View of Data
1.2.1 Levels of Data Abstraction
- View Level:
- how the data items in DB are used by different users
- Logical Level:
- e.g. Relational Table
- Physical Level:
- storage structure and access methods, such as index, physical blocks, access methods for secondary memory.
1.2.2 Instances and Schemas
- Instances: The collection of information stored in the database at a particular moment.
- Schemas: The overall design of the database.
1.2.3 Data Model
DBS中对数据组织与管理/使用方式的抽象描述,包括
- 数据组织的语法定义,如数据项、数据项间的联系
- 数据组织的语义定义,如完整性约束
- 数据操作 (note: only in some data models, e.g. relational data model)
- Relational Data Model
All the data is stored in various tables.
- Entity-Relationship model
Using the entity and the relationship to model the object and the association among objects
E-R Diagram
1.2.4 Data Independence
- 逻辑模式→内模式/物理模式间的映射与physical data independence
- 外模式→逻辑模式间的映射与logical data independence
上述两者均通过调整映射关系保证上级不发生改变
1.4 Database Language
DML: DML is the language that enables users to access or manipulate the data as organized by the appropriate data model Two types of DML:
- procedural (过程性) – user specifies what data is required and how to get those data
- nonprocedural (说明性,declarative) – user specifies what data is required without specifying how to get those data
DDL:Data definition language
DCL: Data Control language
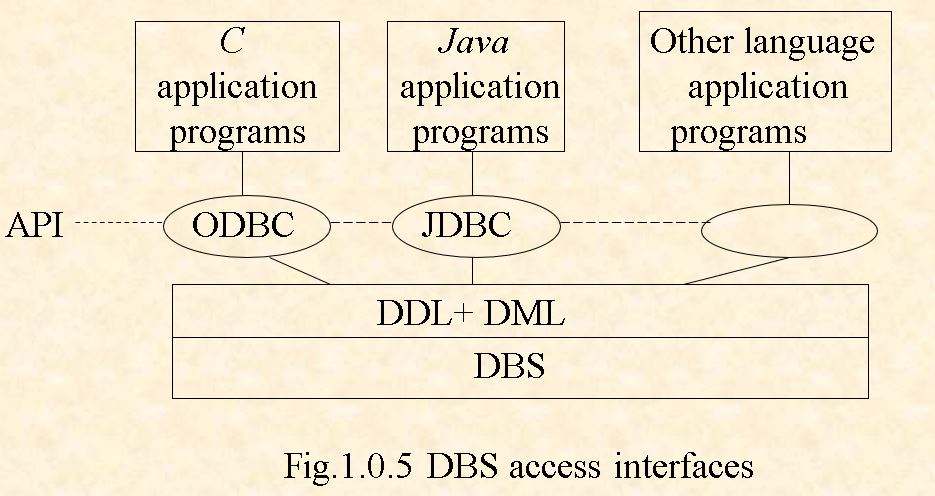
1.5 DB Access for Application Programs
Chapter 2 Introduction to the Relational Model
2.1 Structure of Relational Databases
- Basic structure
- Attributes (columns)
- tuples (rows)
2.2 Database schema
- Relation schema
- Relation instance
2.3 Keys (键、码)
super key: a subset of R where no two distinct tuples in relation r(R) have the same values on all attributes in K.
candidate key: minimal super key(可以为空)
- primary attribute: the attributes in the candidate keys
- non-primary attribute:
primary key: 主键(不可以为空)
主键约束:主键中的数值互不相同 关系表主键的选择方式:尽量选择数值型的候选键
foreign key(外键关联的概念):在本表r1中不为候选键,但在别的表r2中为主键(外键参照关系)
- 参照关系和被参照关系
- 关系模式图
- 外键参照性约束:在参照关系表中出现的外键必须在被参照关系表中出现
note: 在进行实验的时候,首先先导入被参照关系表,再建立参照关系表。
2.4 Schema Diagrams
A database schema, along with primary key and foreign key dependency.
- node schema, attributes, primary key
- directed arc foreign key dependency
2.5 Relational Query Language
- non-procedural
- fundamental operations
- Selection, Projection, Natural join, Cartesian Product(意义不大, 使用where条件可以避免笛卡尔积), Union.
- additive operations
- extended operations
Chapter 3 Introduction to SQL
3.2 Data Definition
3.2.1 Domain Types Def
属性的类型,看看ppt即可
3.2.2 Schema Definition
- Create
- Insert
- Delete Delete vs Drop Delete:删掉关系模式中的所有元组,但并不删掉schema Drop:不仅删掉关系模式中的所有元组,还删掉schema
- Alter
alter table r drop A
- unique key : 候选键声明方式,值唯一
3.3 Basic structure — Select query
3.3.1 Where clause
3.3.2 From clause
3.3.3 Natural Join
3.3.4 The rename operation
Other:
- string operation: %aaa%, _ _ _
- order by: asc(default) or desc
- between
- distinct
Some Example:
3.5 Set Operations
- Union
- Intersect
- except
Classical Example:
3.7 Aggregate Functions
- avg: average value,
- min: minimum value,
- max: maximum value,
- sum: sum of values,
- count: number of values — include value NULL
- Aggregate with Grouping
- Having clause predicates in the having clause are applied after the formation of groups whereas predicates in the where clause are applied before forming groups.
3.8 Nested Subquries
The subquery is often nested in the where clause/having clause, from clause
3.8.1 Set Membership
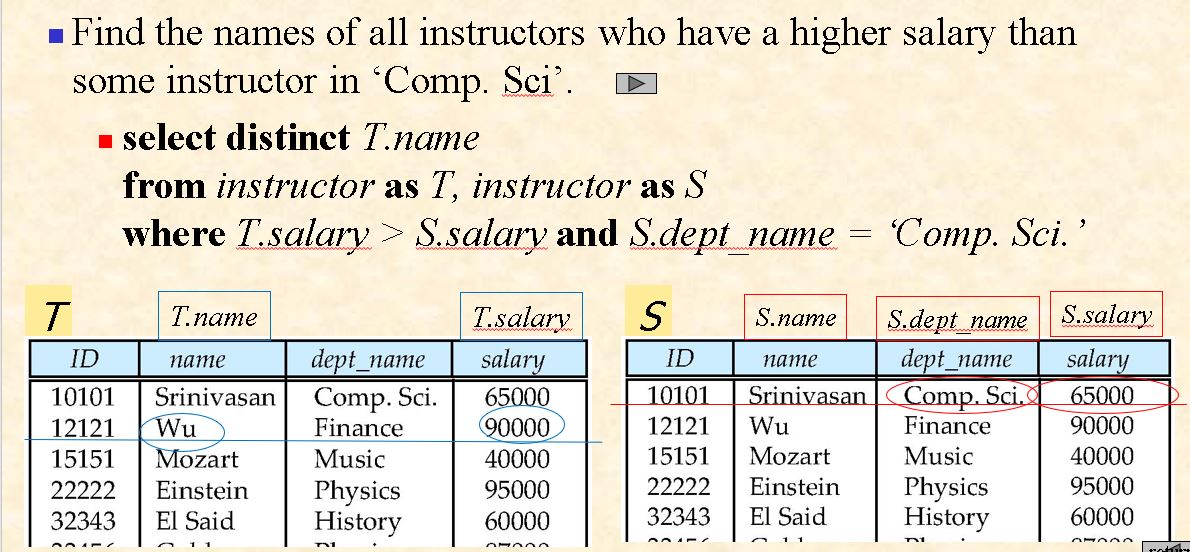
3.8.2 Set Comparison – “some” Clause
some: